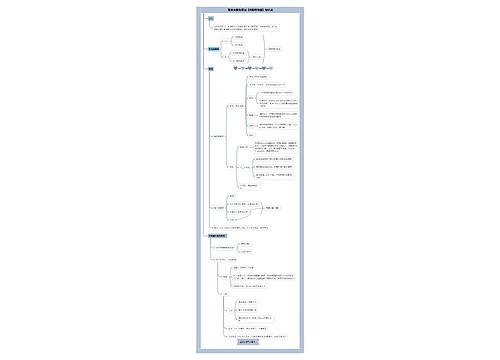
Chapter2 Phonology思维导图

Chapter2 Phonology
树图思维导图提供 Chapter2 Phonology 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 Chapter2 Phonology 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:4e514fd4aab4c5b625cd0285b4944a3a
思维导图大纲
Chapter2 Phonology思维导图模板大纲
The phonic medium of language; the sounds that are produced by humans through their speech organs and have a role to play in linguistic communication, these sounds are limited in number
The phonic medium of language
limited rangeof sounds which are meaningful in human communication
The speech sounds
the individual sounds within this range
Phonology
Phonology(音位学)and phonetics(语音学)
Similarity
both are concerned with the same aspect of language-the speech sounds
Differences
phonetics: general; interested in all the speech sounds used in all human languages
phonology: specific; aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistics communication
Phone(音素),phoneme(音位),and allophone(音位变体)
Phone
A phone is a phonetic unit or segment
The speech sounds we hear and produce during linguistic Phone communication are all phones
Phoneme
A phoneme is a phonological unit; it is a unit that is of distinctive value (the smallest linguistic unit of sound that can signify a differencd in meaning)
It is an abstract unit, not a particular sound, but it is represented by a certain phone in certain phonetic context
Allophone
The different phones that can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments, that is, any of the different forms of a phoneme
Phonemic contrast (音位对立),complementary distribution(互补分布),and minimal pair(最小对立体)
Phonemic contrast
two distinctive phonemes
/p/&/b/ in [pit] & [bit]
Complementary distribution
allophones of the same phoneme they do not distinguish meaning, but complement each other in distribution
/p/:unaspirated[p]&aspirated[p]
Minimal pair
When two different forms are identical in form except for sound segment which occurs in the same place in the strings, the two sound combinations are said to form a minimal pair
Minimal set (最小对立集)
All these sound combinations together constitute a minimal set; they are identical in form except for the initial consonant
Some rules in phonology
Sequential rules (序列规则)
a sound-pattern rule that determine which phonemes can begin a word, end a word and follow each other
Rule1: If a word begins with a [I] or a [r], then the next sound must be a vowel
Rule2: If three consonants should cluster together at the beginning of a word, the combination should obey the following a rules
Rule3: The rule governing the phonological patterning are language-specific. What is not permissible in English might be permissible in another language
Assimilation rule (同化规则)
assimilates one sound to another by "copying" a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the phones similar
Vowels are nasalized in certain phonetic contexts
Within a word, the nasal [n] assumes the same place of articulation as the consonant that follows it
The sound assimilation is actually reflected in the spelling in most cases
Deletion rule(省略规则)
when a sound is to be deleted although it is orthographically represented
E.g delete a [g] when it occurs before a final nasal consonant
E.g. the regular deletion of the [b]
Suprasegmental features (超音段特征)-stress(重音),tone(音调),intonation (语调)
Suprasegmental features: The phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments
Stress
refer to the degree of force used in producing a syllable
word stress
The location of stress in English distinguishes meaning
A shift of stress may change the part of speech of a word from a noun to a verb although its spelling remains unchanged
Similar alternation of stress also occurs between a compound noun and a phrase consisting of the same elements
The meaning-distinctive role played by word stress is also manifested in the combinations of -ing forms and nouns
sentence stress
Refer to the relative force given to the components of a sentence
Tone
pitch variations, which are caused by the differing rates of vibration of the vocal cords
English is not a tone language, but Chinese is
level(阴平)
rise (阳平)
fall-rise (上声)
fall(去声)
Intonation
Definition
when pitch, stress and length variations are tied to the sentence rather than the word in isolation
Types of intonation
the falling tone
matter of fact
the rising tone
doubts or questions
the fall-rise tone
implied message
the rise-fall tone
emphasis
Phonetics
Definition
the study of the phonic medium of language
articulatory phonetics 发音语音学
how a speaker uses his speech organs to articulate the sounds
auditory phonetics 听觉语音学
how the sounds are perceived by the hearers
acoustic phonetics 声觉语音学
the physical means by which sounds are transmitted through the air from one person to another
Organs of speech
the pharyngeal cavity 咽腔-the throat
vibration of the vocal cords
all vowels
voiced consonants 浊辅音
without vibration
voiceless consonants 清辅音
the oral cavity 口腔-the mouth
the tongue (the most flexible)
the uvula 小舌
the soft palate (the velum)软腭
the hard palate 硬腭
the teeth ridge (the alveolus)齿龈
the teeth
the lips
the nasal cavity鼻腔-the nose
not nasalized
all vowels
most consonants
nasalized
[m]. [n],[ŋ]
Orthographic representation of speech sounds-broad and narrow transcriptions
broad transcription 宽式标音
the transcription with letter-symbols only, normally used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks for general purposes
narrow transcription 严式标音
the transcription with letter-symbols together with the diacritics, used by the phoneticians in their study of speech sound
Classification of English speech sounds
consonants
the airstream is blocked somewhere or somehow
Classification of English consonants
voicing
voiced consonants
causing vibration of vocal cords
[b]
voiceless consonants
without causing vibration of vocal cords
[p]
manner of articulation
stops 闭塞音
[p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g]
fricatives 摩擦音
[f], [v], [s],[z],[ʃ],[3],[θ], [ð], [h]
affricates 塞擦音
[tʃ]、[dʒ]
liquids流音
[l]、[r]
nasals 鼻音
[m]、[n]、[ŋ]
glides 滑音
[j]、[w]
place of articulation
bilabial 双唇音
[p], [b], [m], [w]
labiodental 唇齿音
[f], [v]
dental 齿音
[θ]、[ð]
alveolar 齿龈音
[d]、[s]、[z]、[n]、[l]、[r]
palatal 硬腭音
[ʃ]、[ʒ]、[tʃ]、[dʒ]、[j]
velar软腭音
[k]、[g]、[ŋ]
glottal 喉音
[h]
[p],[b],[g]
vowels
the airstream meets with no obstruction of any kind
Classification of English vowels
the position of the tongue in the mouth
front
The one in the production of which the front part of the tongue maintains the highest position [i:]、[i]、[ɑ]、[e]、[æ]
central
It is produced when the central part of the tongue is held highest [ə]、[ʒ]、[ʌ]
back
It is produced when we raise the back of the tongue higher than the rest of it [u:], [u], [ɔ:], [a:]
the openness of the mouth
close vowels 闭元音
[i:]、[i]、[u:]、[u]
semi-close vowels 半闭元音
[e]、[ʒ]
semi-open vowels 半开元音
[ə]、[ɔ]
open vowels 开元音
[æ]、[ʌ]、[a]、[a:]
the shape of the lips
rounded 元唇音
[u:]、[u]、[ɔ:]
unrounded 非元唇音
[i:]、[i]、[e]、[ʒ]、[ə]、[æ]、[ʌ]、[a]
the length of the vowels
long/tense
short/lax
monophthongs
a vowel sound that throughout its duration has a single constant monophthongs articulatory E.g. [i]
diphthongs
a single-syllable vowel sound in which the beginning of the sound is diphthongs different from the end [ei]、[ai]、[ɔi]、[əu]、[au]、[iə]、[εə]、[uə]
[e]、[i]、[ai]、
相关思维导图模板

树图思维导图提供 Session one: Phonology and Phonetics 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 Session one: Phonology and Phonetics 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:9522372b570baacdc9cfe8696e52d96a


树图思维导图提供 Phonology 音位学思维导图 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 Phonology 音位学思维导图 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:ecae8f95762d98fe4bc8c3fe109453f4





 上海工商
上海工商