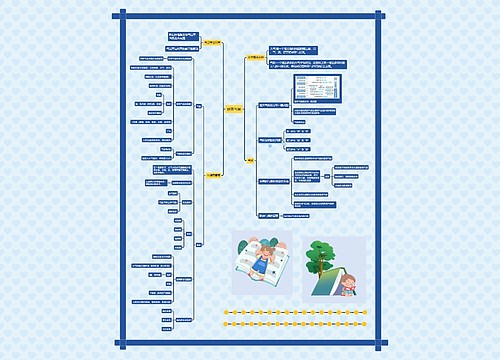
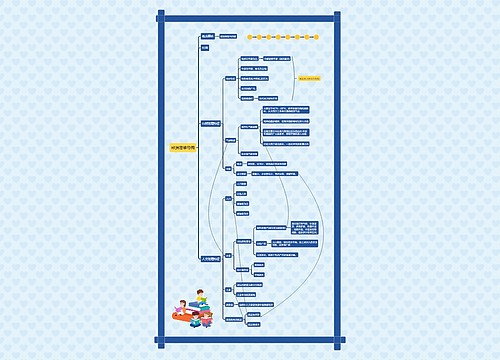
Unit 10: Living Things思维导图
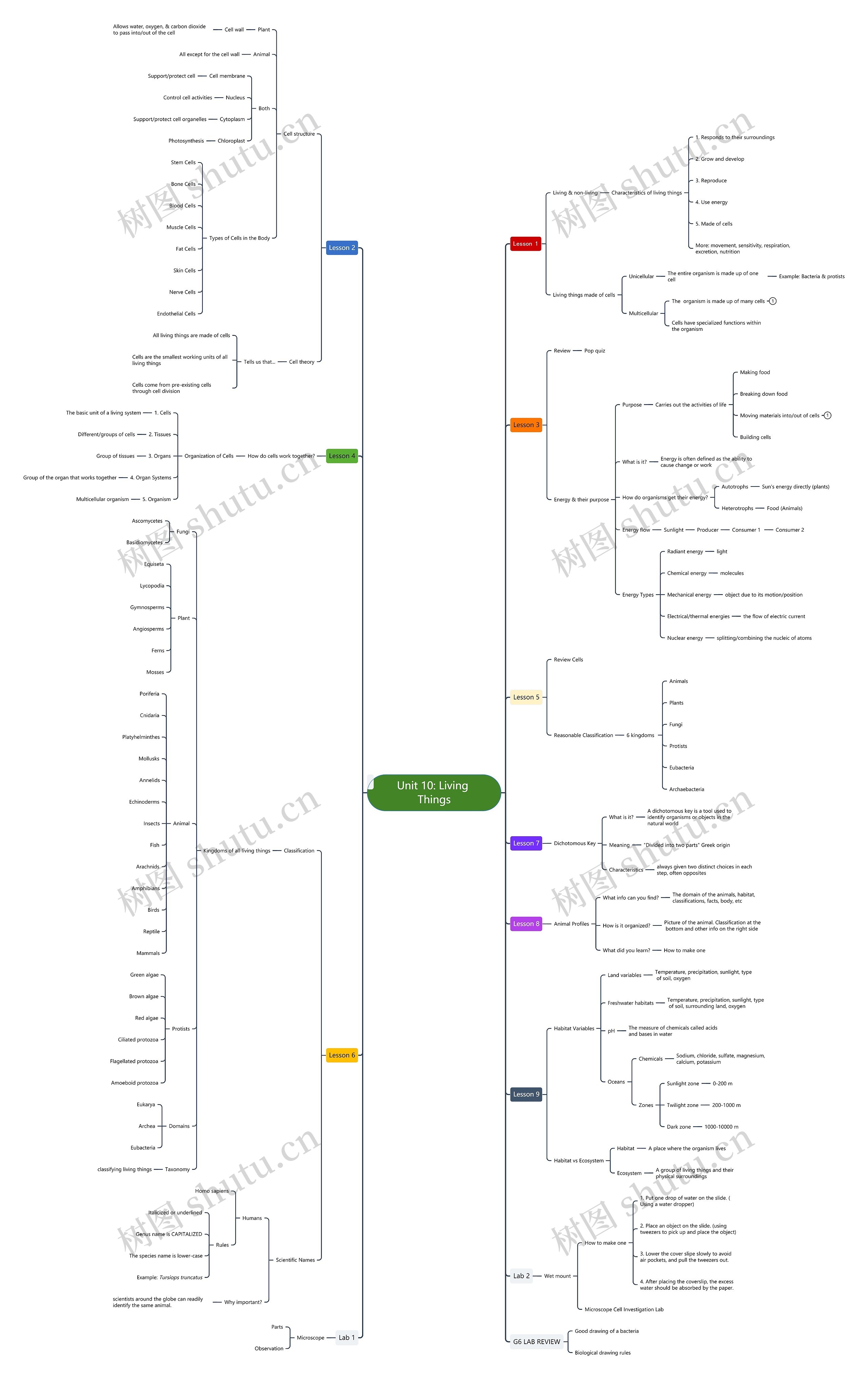
Unit 10: Living Things
树图思维导图提供 Unit 10: Living Things 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 Unit 10: Living Things 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:a9baa6e6a4316e71085600e049384418
思维导图大纲
Unit 10: Living Things思维导图模板大纲
Lesson 1
Living & non-living
Characteristics of living things
1. Responds to their surroundings
2. Grow and develop
3. Reproduce
4. Use energy
5. Made of cells
More: movement, sensitivity, respiration, excretion, nutrition
Living things made of cells
Unicellular
The entire organism is made up of one cell
Example: Bacteria & protists
Multicellular
The organism is made up of many cells
子主题 1
Cells have specialized functions within the organism
Lesson 2
Cell structure
Plant
Cell wall
Allows water, oxygen, & carbon dioxide to pass into/out of the cell
Animal
All except for the cell wall
Both
Cell membrane
Support/protect cell
Nucleus
Control cell activities
Cytoplasm
Support/protect cell organelles
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis
Types of Cells in the Body
Stem Cells
Bone Cells
Blood Cells
Muscle Cells
Fat Cells
Skin Cells
Nerve Cells
Endothelial Cells
Cell theory
Tells us that...
All living things are made of cells
Cells are the smallest working units of all living things
Cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division
Lesson 3
Review
Pop quiz
Energy & their purpose
Purpose
Carries out the activities of life
Making food
Breaking down food
Moving materials into/out of cells
子主题 1
Building cells
What is it?
Energy is often defined as the ability to cause change or work
How do organisms get their energy?
Autotrophs
Sun's energy directly (plants)
Heterotrophs
Food (Animals)
Energy flow
Sunlight
Producer
Consumer 1
Consumer 2
Energy Types
Radiant energy
light
Chemical energy
molecules
Mechanical energy
object due to its motion/position
Electrical/thermal energies
the flow of electric current
Nuclear energy
splitting/combining the nucleic of atoms
Lesson 4
How do cells work together?
Organization of Cells
1. Cells
The basic unit of a living system
2. Tissues
Different/groups of cells
3. Organs
Group of tissues
4. Organ Systems
Group of the organ that works together
5. Organism
Multicellular organism
Lesson 5
Review Cells
Reasonable Classification
6 kingdoms
Animals
Plants
Fungi
Protists
Eubacteria
Archaebacteria
Lesson 6
Classification
Kingdoms of all living things
Fungi
Ascomycetes
Basidiomycetes
Plant
Equiseta
Lycopodia
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Ferns
Mosses
Animal
Poriferia
Cnidaria
Platyhelminthes
Mollusks
Annelids
Echinoderms
Insects
Fish
Arachnids
Amphibians
Birds
Reptile
Mammals
Protists
Green algae
Brown algae
Red algae
Ciliated protozoa
Flagellated protozoa
Amoeboid protozoa
Domains
Eukarya
Archea
Eubacteria
Taxonomy
classifying living things
Scientific Names
Humans
Homo sapiens
Rules
Italicized or underlined
Genus name is CAPITALIZED
The species name is lower-case
Example: Tursiops truncatus
Why important?
scientists around the globe can readily identify the same animal.
Lesson 7
Dichotomous Key
What is it?
A dichotomous key is a tool used to identify organisms or objects in the natural world
Meaning
"Divided into two parts" Greek origin
Characteristics
always given two distinct choices in each step, often opposites
Lesson 8
Animal Profiles
What info can you find?
The domain of the animals, habitat, classifications, facts, body, etc
How is it organized?
Picture of the animal. Classification at the bottom and other info on the right side
What did you learn?
How to make one
Lesson 9
Habitat Variables
Land variables
Temperature, precipitation, sunlight, type of soil, oxygen
Freshwater habitats
Temperature, precipitation, sunlight, type of soil, surrounding land, oxygen
pH
The measure of chemicals called acids and bases in water
Oceans
Chemicals
Sodium, chloride, sulfate, magnesium, calcium, potassium
Zones
Sunlight zone
0-200 m
Twilight zone
200-1000 m
Dark zone
1000-10000 m
Habitat vs Ecosystem
Habitat
A place where the organism lives
Ecosystem
A group of living things and their physical surroundings
Lab 2
Wet mount
How to make one
1. Put one drop of water on the slide. (Using a water dropper)
2. Place an object on the slide. (using tweezers to pick up and place the object)
3. Lower the cover slipe slowly to avoid air pockets, and pull the tweezers out.
4. After placing the coverslip, the excess water should be absorbed by the paper.
Microscope Cell Investigation Lab
G6 LAB REVIEW
Good drawing of a bacteria
Biological drawing rules
Lab 1
Microscope
Parts
Observation
思维导图模板大纲
相关思维导图模板

树图思维导图提供 3A Unit 1 A Proper Job 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 3A Unit 1 A Proper Job 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:8d966446cda22e33b426cba15d3d981e

树图思维导图提供 双重循环--C++第10课 在线思维导图免费制作,点击“编辑”按钮,可对 双重循环--C++第10课 进行在线思维导图编辑,本思维导图属于思维导图模板主题,文件编号是:82c73cb7b116c51834732b79206334eb




 上海工商
上海工商